 |
 |
 |
 |
| APPENDIX E |

Description: Uniformly black or dark brown with a small, narrow head.
Characteristics: A viper that does not look like one. It is small in size, and its small head does not indicate the presence of venom glands. It has a rather inoffensive disposition; however, it will quickly turn and bite if restrained or touched. Its venom is a potent hemotoxin for such a small snake. Its fangs are exceptionally long. A bite can result even when picking it up behind the head. It is best to leave this snake alone.
Habitat: Agricultural areas and arid localities
Length: Average 55 centimeters, maximum 75 centimeters
Distribution: Sudan, Ethiopia, Somaliland, Kenya, Tanganyika, Uganda, Cameroon, Niger, Congo, and Urundi.
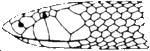

Description: Olive to rusty brown with a dark V-shaped mark on the head and a brown, zigzag band along the back.
Characteristics: The Palestinian viper is closely related to the Russell's viper of Asia. Like its cousin, it is extremely dangerous. It is active and aggressive at night but fairly placid during the day. When threatened or molested, it will tighten its coils, hiss loudly, and strike quickly.
Habitat: Arid regions, but may be found around barns and stables. It has been seen entering houses in search of rodents.
Length: Average 0.8 meter, maximum 1.3 meters.
Distribution: Turkey, Syria, Palestine, Israel, Lebanon, and Jordan.
| Updated: 12 January 2008 |
|
Born on 29 January 2000 |